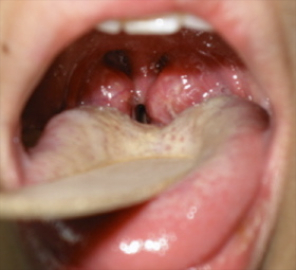
Tonsils and Adenoids
There are several variations of tonsillitis: acute, recurrent, and chronic tonsillitis and peritonsillar abscess.
More About Tonsils, Adenoids, and Tonsilitis
Tonsillitis refers to inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils. The inflammation may involve other areas of the back of the throat including the tonsils and adenoids and the lingual tonsils (areas of tonsil tissue at the back of the tongue). There are several variations of tonsillitis: acute, recurrent, and chronic tonsillitis and peritonsillar abscess.
The type of tonsillitis determines what symptoms will occur:
Acute tonsillitis
Patients have a fever, sore throat, foul breath, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), odynophagia (painful swallowing), and tender cervical lymph nodes.
Recurrent tonsillitis
This diagnosis is made when an individual has multiple episodes of acute tonsillitis in a year.
Chronic tonsillitis
Individuals often have chronic sore throat, bad breath, tonsillitis, and persistently tender cervical nodes.
Peritonsillar abscess
Individuals often have severe throat pain, fever, drooling, foul breath, trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), and muffled voice quality, such as the “hot potato” voice.
Tonsillitis is usually treated with a regimen of antibiotics. Fluid replacement and pain control are important. Hospitalisation may be required in severe cases, particularly when there is airway obstruction.
When the condition is chronic or recurrent, a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils, tonsillectomy, is often recommended.
For some patients, a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils (and adenoids if they cause health issues) is required, which requires a stay in hospital. The tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy surgery is minimally invasive, performed through the throat and with cameras through the nose, and requires a general anaesthetic.
An overnight stay in hospital is required if your child is under 4 years of age. If your child is over the age of 4 then often the procedure can be performed as a day surgery procedure. Here is a link to a quick children’s video
A variety of tools may be used to remove the tonsils and/or adenoids, including harmonic scalpel, plasma dissection, cold dissection, laser and electrocautery. Your surgeon will decide which is the best option for your particular case.
Many patients require around 2 weeks off either school or work to recover from the surgery, with post-operative pain the most concerning symptom.
Video relating to Tonsils and Adenoids
Still have a question?
Our team will be happy to answer any questions you may have about Tonsils and Adenoids.